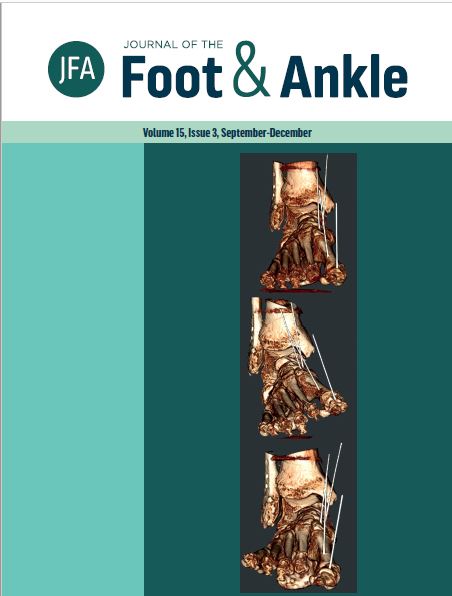
Reliability of coronal plane rotation measurements in the medial column of the foot: a cadaveric study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30795/jfootankle.2021.v15.1598Keywords:
Cadaver, Hallux valgus, Metatarsal bones, Pronation, Weight-bearingAbstract
Objective: To assess interobserver reliability of previously described coronal plane rotation measurements of medial column bones and to assess their ability to accurately quantify changes in rotational profile. Methods: Two cadaveric below-knee specimens were implanted with pins in each bone of the medial column. Weight-bearing computed tomography (CT) scans were acquired in a simulated standing position under neutral, supinated, and pronated conditions. For each specimen and condition, 2 observers measured the coronal plane rotation of the navicular, medial cuneiform, first metatarsal base, shaft, and head, and proximal phalanx of the hallux as previously described. The rotation of each pin was measured relative to the ground in the coronal plane for each condition. These measurements were defined as benchmarks for the rotational profile of each bone. The correlation between these benchmarks and direct bone measurements was then assessed. Intraclass correlation coeficiente was used to assess interobserver reliability. Pearson’s coefficient was used to evaluate correlations. Results: The interobserver reliability of direct bone measurements ranged from 0.98 to 0.99. Correlations between pin rotation and direct measurements ranged from ρ=0.87 to 0.99 across the neutral, supinated, and pronated conditions. Conclusion: Coronal plane rotation measurements of medial column bones described in this study are reliable tools. Level of Evidence III; Case-Control Study.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Foot & Ankle

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.